An Inferior Mi Affects Which of the Following
The injury current in RCA occlusion is directed inferiorly and rightward producing ST elevation in lead III lead II as lead. Reperfusion bradycardia Ischemic AV nodal arrhythmias are some times very difficult to differentiate from vagotonia especially if occur within 24h.
Stemi Heart Attacks The Real Dangers Myheart
A posterior STEMI is the back wall of the heart.

. However due to recent developments in reperfusion techniques in. The plaque detaches from the wall of the artery effectively blocking it. During the first 30 days after a myocardial infarction death can occur due to cardiogenic shock sudden cardiac death heart failure mechanical cardiac complications or another MI event.
This is a quiz that contains NCLEX questions for myocardial infarction MI. Myocardial infarction is defined as sudden ischemic death of myocardial tissue. When used as an antiarrhythmic drug lidocaine typically.
When specifying the location of myocardial infarction reference is being made to the left ventricle. The collaborative expert consensus of the European Society of Cardiology ESCAmerican College of Cardiology ACCAmerican Heart Association AHA and World Heart Federation WHF released the fourth universal definition of Myocardial Infarction MI in August 2018. The EKG also provides information as to which part of the heart the blocked artery is supplying for example an anterior vs.
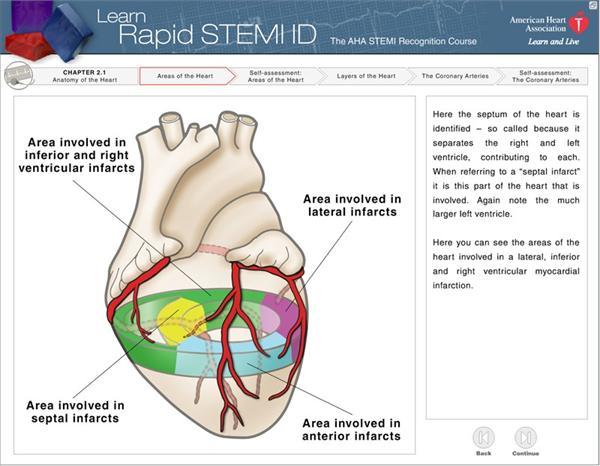
This is sometimes termed poor R wave progression or PRWP. Pain radiates most often to the left arm but may also radiate to the lower jaw neck right arm back and upper abdomen. Inferior wall of the heart strictly speaking there is no walls for heart only surfaces which blends with adjacent areas inferior wall is formed by diaphragmatic surface and posterior surfaceInferior MI can occur by either RCA or LCX obstructionThe outcome of inferior MI is determined by mainly by the extent of LV myocardial damage it inflictsTo quantitate this we.
A 36-year-old woman with a history of poorly controlled thyrotoxicosis has. The classic features of inferior STEMI are unmistakable. As the flow of blood slows the oxygen-hungry heart muscles begin to die often causing sudden pain.
When an inferior MI extends to posterior regions as well an associated posterior wall MI may occur. Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms of acute myocardial infarction and is often described as a sensation of tightness pressure or squeezing. These include AV block atrial arrhythmias profound hypotension and bradycardia and pericarditis.
For this purpose the left ventricle is subdivided into 4 walls. However several complicating factors can lead to increased mortality including right ventricular infarction hypotension bradycardia heart block and cardiogenic shock. The mortality rate of an inferior wall MI is less than 10 percent.
In the clinical context myocardial infarction is usually due to thrombotic occlusion of a coronary vessel caused by rupture of a vulnerable plaque. Usually an inferior myocardial infarction is associated with the loosening of an atherosclerotic plaque in the wall of the right coronary artery. A myocardial infarction happens there is not enough blood flow to the heart muscle which causes cells to die.
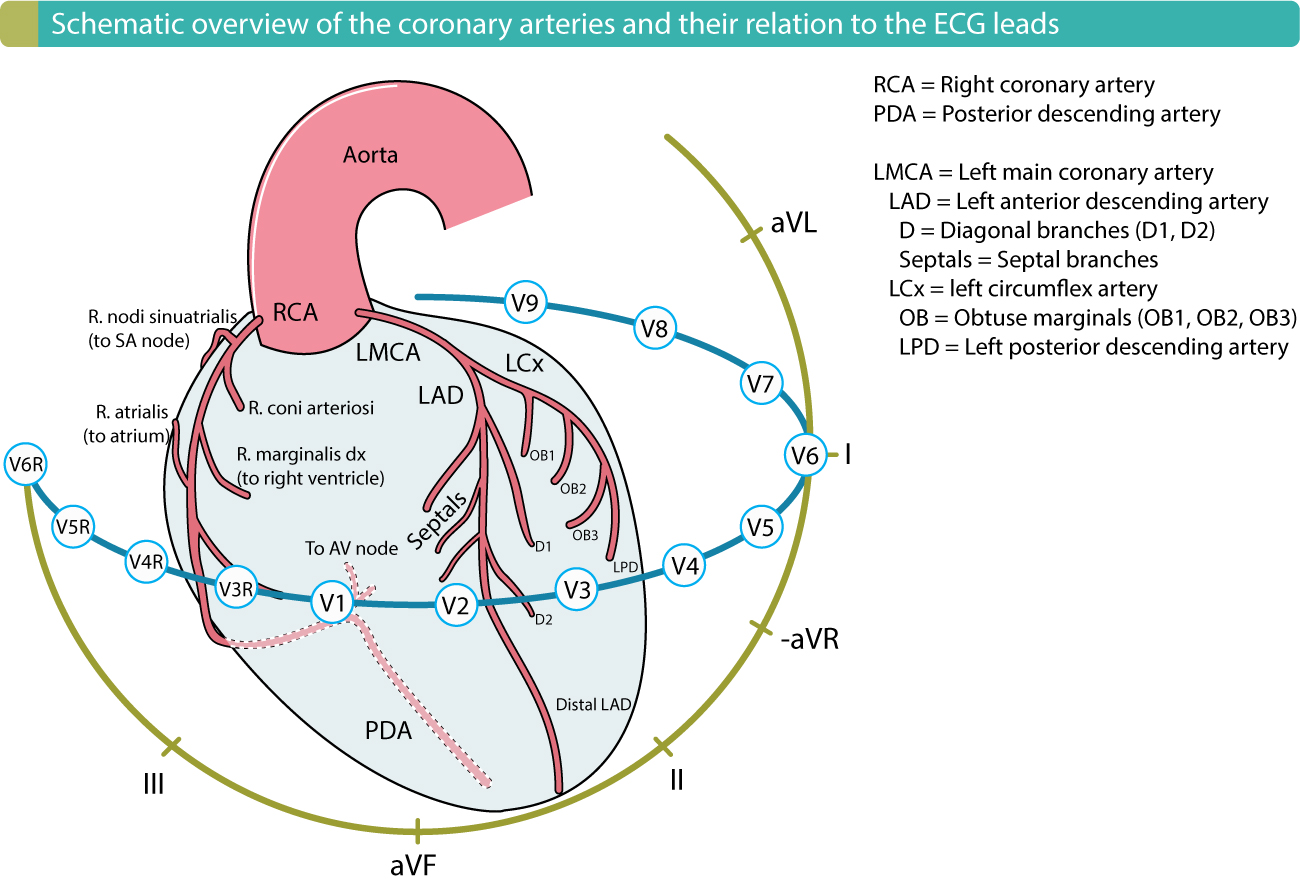
The RCA territory covers the medial part of the inferior wall including the inferior septum. In most cases there is reciprocal ST-segment depression in the high lateral or superior. While both RCA and LCx occlusion may cause infarction of the inferior wall the precise area of infarction and thus ECG pattern in each case is slightly different.
Drug effects -Like morphine. An anterior STEMI is the front wall of the heart and the most serious. An inferior STEMI is the bottom wall of the heart.
Ischemia induces profound metabolic and ionic perturbations in. Inferior anterior lateral and septal wall Figure 2 below. Patients with inferior wall MI and accompanying RVMI have a much higher rate of complications than patients with inferior wall MI without RV involvement accounting for part of the adverse prognostic implications of RVMI Box 145.
Acute myocardial infarction MI involving only the right ventricle is an uncommon event. Location of acute myocardial infarction refers to the area of the left ventricle. However several complicating factors that increase mortality including right ventricular infarction hypotension bradycardia heart block and cardiogenic shock.
A posterior STEMI vs. The hallmark is the presence of ST-segment elevations in the inferior limb leads II III and aVF. The ECG findings of an old anterior myocardial infarction include.
Diagnosis of type I MI focuses on the detection of a rise andor fall of cardiac Troponin. Necrosis of AV node. When used as an antiarrhythmic drug lidocaine typically A Increases action potential duration B Increases contractility C Increases PR interval D Reduces abnormal automaticity.
The ECG findings of an acute inferior myocardial infarction include the following. Inferior wall myocardial infarction IMI is the most common ST-elevation myocardial infarction STEMI. A person who has experienced myocardial infarction MI is likely to experience other cardiovascular events.
The ECG shows an inferior myocardial infarction and ventricular tachycardia. The ECG findings of an acute inferior myocardial infarction include the following. This can lead to complications such as pericarditis heart failure rupture and more.
With chest pain and a fast irregular heart rhythm. More often right ventricular MI RVMI is associated with acute ST-elevation MI of the inferior wall of the left ventricle and occurs in 30 to 50 percent of such cases RVMI is associated with higher in-hospital morbidity and mortality compared with patients. A 57-year-old man is admitted to the emergency department with chest pain and a fast irregular heart rhythm.
Loss of anterior forces leaving Q waves in leads V1 and V2. The mortality rate of an inferior wall MI is less than 10. SA and AV block occur due to various mechanisms in inferior MI.
The ECG shows an inferior myocardial infarction and ventricular tachycardia. ST segment elevation in the inferior leads II III and aVF Reciprocal ST segment depression in the lateral andor high lateral leads I aVL V5 and V6. An inferior wall MI also known as IWMI or inferior MI or inferior ST segment elevation MI or inferior STEMI occurs when inferior myocardial tissue supplied by the right coronary artery or RCA is injured due to thrombosis of that vessel.
Ischemia of SAAV node. Then heart muscle cells die the tissue become necrotic. An inferior myocardial infarction refers to an infarction located in the inferior wall of.
Ecg Localization Of Myocardial Infarction Ischemia And Coronary Artery Occlusion Culprit Ecg Echo

Inferior Wall St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Mi Ecg Review Learn The Heart
0 Response to "An Inferior Mi Affects Which of the Following"
Post a Comment